Atili et al 2019
Calcium-induced differentiation in normal human colonoid cultures: Cell-cell / cell- matrix adhesion, barrier formation and tissue integrity
D Attili, SD McClintock, AH Rizvi, S Pandya, H Rehman, DM Nadeem, A Richter, D Thomas, MK Dame, DK Turgeon, J Varani, MN Aslam
Published: PLoS ONE 14(4): 2019
Background:
Progression from initial polyp formation to more serious disease is difficult to study experimentally since colonic polyps are removed upon detection. Colonoid culture technology provides a way to study human colon polyp responses to potentially useful compounds under ex-vivo conditions.
The goal of the study was to assess calcium alone against Aquamin for capacity to affect growth and differentiation in colonoid cultures derived from histologically-normal human colon tissue (n=5).
Methods:
Colonoid cultures were maintained in a low-calcium (0.25 mM) medium or in medium supplemented with an amount of calcium (1.5–3.0 mM), either from calcium alone or Aquamin for two weeks.. Changes in growth, morphological features and protein expression profiles were then assessed using a combination of phase-contrast, scanning electron & transmission-electron microscopy, histology and immunohistology, & proteomic assessment.
Conclusions :
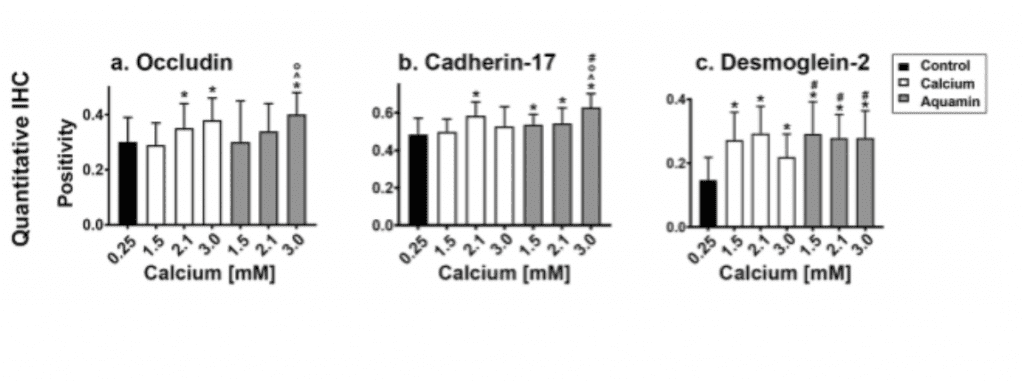
Here we show in colonoids derived from histologically-normal tissue that extensive differentiation occurred in the absence of intervention, and that treatment with either calcium alone or Aquamin had only a modest additional effect in the gross and histological appearance of normal tissue-derived colonoids. Additionally, there was a strong induction of several proteins that contribute to cellular adhesive functions, barrier formation and tissue integrity.
This is in contrast to previous studies in adenoma colonoids where Aquamin suppressed growth and induced features of differentiation not seen with calcium alone at a comparable level (McClintock et al., 2018).
Figure:
Colonoid appearance in culture: Histological features. At the end of the incubation period, colonoids were examined by light microscopy
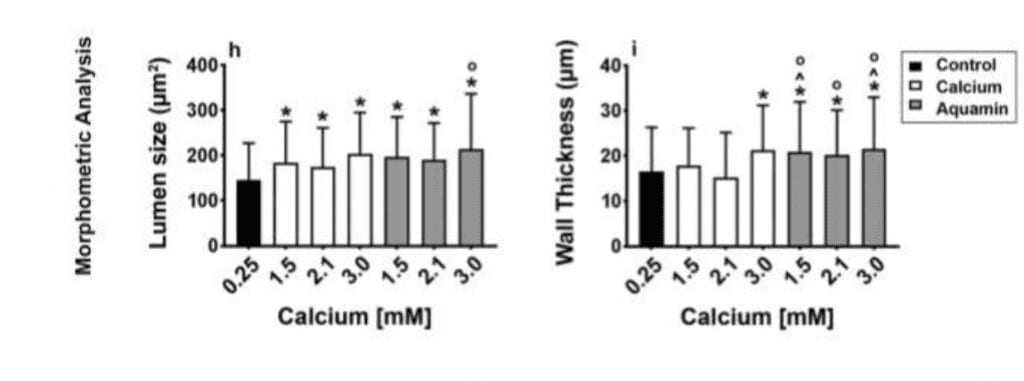
(lower panels) Cell surface components were examined between colonoids.
PUBLISHED ARTICLES
Sherk et al., 2017
Calcium Supplementation Attenuates Disruptions in Calcium Homeostasis during Exercise VD Sherk, SJ Wherry, DW Barry, KL Shea, P Wolfe, WM Kohrt Med Sci Sports Exerc., 49(7), 1437–1442, 2017 Background: Exercise can lead to a decrease in calcium levels during prolonged moderate-to- vigorous endurance
Lee et al., 2010
The effects of a Mineral Supplement (Aquamin F) and its Combination with Multi-Species, Lactic-Acid Bacteria on Bone accretion in an Ovariectomized Rat Model Lee et al., Cell Biotech, Republic of Korea, J. Exp. Biomed. Sci. 2010, 16(4) The Rat ovariectomised (OVX) model is
Aslam et al., 2010
A mineral-rich extract, Aquamin, from the red marine algae, Lithothamnion calcareum, preserves bone structure and function in female mice on a high fat diet. MN Aslam, JM Kreider, T Paruchuri, N Bhagavathula, M DaSilva, R Zernicke, S Goldstein and J Varani, University of Michigan,
Aslam et al., 2013
A multi-mineral-rich natural product from red marine algae preserves bone structure and function in C57BL/6 Mice MN Aslam, M Naik, I Bergin, K Jepsen, JM Kreider, KH Graf, SA Goldstein & J Varani Depts of Pathology & Orthopaedic Surgery, University of Michigan, USA
Slevin et al. 2014
Effect of supplementation with short-chain fructo-oligosaccharide and Aquamin on bone mineral density and bone turnover markers in post-menopausal women: A 24 month double blind, randomised controlled study.
Barry et al. 2011
Acute Calcium Ingestion Attenuates Exercise-Induced Disruption of Calcium Homeostasis
Shea et al. 2014
Calcium supplementation and PTH response to vigorous walking in postmenopausal women
Zenk et al. 2017
Effect of calcium derived from Lithothamnion sp on markers of calcium metabolism in premenopausal women.
Bae et al. 2011
Magnesium Supplementation through Seaweed Calcium Extract Rather than Synthetic Magnesium Oxide Improves Femur Bone Mineral Density and Strength in Ovari-ectomized Rats
O’Gorman et al. 2012
The Marine-derived, Multi-Mineral Formula, Aquamin, Enhances Mineralisation of Osteoblast Cells In Vitro
Widaa et al. 2014
The osteogenic potential of the marine-derived multi-mineral formula Aquamin in enhanced by the presence of Vitamin D
Aslam et al. 2016
Bone structure & function in male C57BL/6 mice: Effects of a high-fat Western-style diet with or without trace minerals.
Brennan at al. 2015
Incorporation of the natural marine multi-mineral dietary supplement Aquamin enhances osteogenesis and improves the mechanical properties of a collagen-based bone graft substitute
Brennan et al. 2017
A natural, calcium-rich marine multi-mineral complex preserves bone structure composition and strength in an ovariectomised rat model of osteoporosis.
Ryan et al., 2011
Evidence that the marine-derived multi-mineral, Aquamin, has anti-inflammatory effects on cortical glial-enriched cultures. S Ryan, DM O’Gorman, YM Nolan, University College Cork, Ireland Phytotherapy Research (2011) 25:765-7. Cytokines are a family of molecules that help to regulate the immune response and inflammation. Abnormal
O’Gorman et al., 2012
Evidence that the multi-mineral, Aquamin inhibits the NF-κB signalling pathway in-vitro. DM O’Gorman, C O’Carroll, RJ Carmody, University College Cork, Ireland Phytotherapy Research: (2012) 26:630-632 NFκB (Nuclear Factor kappa B) plays a key role in regulating the immune response to inflammation. Incorrect regulation of
O’Callaghan et al., 2013
Antioxidant and Pro-Apoptotic Effects of Marine-Derived, Multi-Mineral Aquamin Supplemented with Pine Bark Extract, Enzogenol, and Green Tea Extract, Sunphenon YC O’Callaghan, E Drummond, DM O’Gorman, and NM O’Brien J Medicinal Foods (2013) AquaPT provides a high level of polyphenols. Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory pathways
Heffernan et al 2020
Mineral rich algae with pine bark improved pain, physical function and analgesic use in mild-knee joint osteoarthritis, compared to Glucosamine: A randomized controlled pilot trial
Cronin et al 2016
Effects of supplementation with a calcium-rich marine-derived multi-mineral supplement and short-chain fructo-oligosaccharides on serum lipids in postmenopausal women
Frestedt et al. 2008
A natural mineral supplement provides relief from knee osteoarthritis symptoms: a randomized controlled pilot trial
Frestedt et al. 2009
A natural seaweed derived mineral supplement (Aquamin F) for knee osteoarthritis: A randomized, placebo-controlled pilot study
Hampton et al 2015
Ulcerative dermatitis in C57BL/6NCrl mice on low-fat and high-fat diets with and without a mineralized red algae supplement
Murphy et al 2014
The marine–derived, multi-mineral formula, AquaPT reduces TNF-α levels in osteoarthritis patients
Varani et al., 2022
Cell-Matrix Interactions Contribute to Barrier Function in Human Colon Organoids James Varani, Shannon D. McClintock and Muhammad N. Aslam*The Department of Pathology, The University of Michigan Medical School, Ann Arbor, MI, United States Background: The gastrointestinal tract barrier can be compromised in various
Aslam et al., 2021
A MULTI-MINERAL INTERVENTION TO MODULATE COLONIC MUCOSAL PROTEIN PROFILE: Results from a 90-day trial in healthy human subjectsAslam et al., Nutrients 2021 Background: Previous studies have shown the digestive health benefits of Aquamin in animal models, as well as in-vivo and ex- vivo culture This study investigated
Aslam et al., 2009
Growth-inhibitory effects of Aquamin, a mineralized extract from the red algae, Lithothamnion calcareum, on Ca2+- sensitive and Ca2+-resistant human colon carcinoma cells. MN Aslam, N Bhagavathula,, T Parachuri, X Hu, S Chakrabarty & J Varani University of Michigan, USA Cancer Letters (2009) There
Aslam et al., 2010
A mineralized red algae extract reduces epithelial abnormalities in the gastrointestinal tract of normal mice on a high-fat Western style diet MN Aslam, T Paruchuri, N Bhagavathula and J VaraniUniversity of Michigan, USA Integr Cancer Ther. 2010 Mar;9(1):93-9 This in-vivo study follows on from our
Dame et al., 2011
Human colon tissue in organ culture: calcium and multi-mineral-induced mucosal differentiation MK Dame, I Veerapaneni, N Bhagavathula, M Naik & J Varani University of Michigan Medical School, Michigan, USA In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol. – Animal (2011) 47:32-38 The marine, multi-mineral Aquamin has
Aslam et al., 2012 | Polyp
A multi-mineral natural product from red marine algae reduces colon polyp formation in C57BL/6 Mice MN Aslam, I Bergin, M Naik, T Paruchuri, A Hampton, M Rehman, MK Dame, H Rush & J Varani Department of Pathology, University of Michigan, USA Nutrition and
Aslam et al., 2012 | Liver
A multi-mineral natural product inhibits liver tumor formation in C57BL/6 Mice MN Aslam, I Bergin, M Naik, A Hampton, R Allen, SL Kunkel, H Rush & J Varani Department of Pathology, University of Michigan, USA Biological Trace Elements Research (2012) 147:267-274 This 18
Aviello et al., 2013
Amelioration of chronic spontaneous colitis by a mineral extract from red algae in IL-10 deficient mice is mouse strain dependent Phytotherapy Research 2013S Amu, SP Saunders, G Aviello and PG Fallon Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) incorporates serious illnesses like ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s
Singh et al., 2015
Induction of calcium sensing receptor in human colon cancer cells by calcium, vitamin D and Aquamin: promotion of a more differentiated, less malignant and indolent phenotype N Singh, M. N. Aslam, J. Varani, S. Chakrabarty Southern Illinois University School of Medicine, IL and
McClintock et al., 2018
Calcium-Induced Differentiation of Human Colon Adenomas in Colonoid Culture: Calcium Alone versus Calcium with Additional Trace Elements SD McClintock et al., Cancer Prevention Research, 2018 From the Varani Laboratory at the University of Michigan, Medical School, USA Background: Epidemiological studies have demonstrated a
Crowley et al., 2018
Dietary Supplementation with a Magnesium-Rich Marine Mineral Blend Enhances the Diversity of Gastrointestinal Microbiota EK Crowley, CM Long-Smith, A Murphy, E Patterson, K Murphy, DM O’Gorman, C Stanton and YM Nolan, University College Cork Marine Drugs 2018 Background: Deficiencies in Calcium and Magnesium intake
Aslam et al 2020
Ulcerative Colitis-Derived Colonoid Culture: A Multi-Mineral-Approach to Improve Barrier Protein Expression
Atili et al 2019
Calcium-induced differentiation in normal human colonoid cultures: Cell-cell / cell- matrix adhesion, barrier formation and tissue integrity
McClintock et al 2020
A Calcium-Rich Multi-Mineral Intervention to Modulate Colonic Microbial Communities and Metabolomic Profiles in Humans: Results from A 90-Day Trial
Aslam et al 2019
A Calcium-Rich Multi-Mineral Intervention to Modulate Colonic Microbial Communities and Metabolomic Profiles in Humans: Results from A 90-Day Trial
Zhang et al., 2020 Prenatal Toxicity – China
A study of the genetic and prenatal developmental toxicity potential of lithothamnion sp Z. Ying , T. Ruotao , W. Haili , L. Shuqin , B. Linxiu , L. Xuemin & L. Qing Institute of Toxicology, Shanxi Provincial Center for Disease Control and Prevention,
Zhang et. al 2020- General Toxicity | China
Evaluation of acute and sub-chronic toxicity of lithothamnion sp. in mice and rats Ying Zhanga, *, Ruotao Tiana , Haili Wub , Xuemin Lia , Shuqin Lia , Linxiu Biana Institute of Toxicology, Shanxi Provincial Center for Disease Control and Prevention, Taiyuan, 030012,
Varani et al., 2022 (NASH – Liver)
LIVER PROTEIN EXPRESSION IN NASH MICE ON A HIGH-FAT DIET J Varani, SD McClintock, RN Knibbs, I Harber, D Zeidan, MAH Jawad-Makki & MN Aslam Frontiers in Nutrition, 2022 Background: Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is a leading cause of liver disease globally. It
Brain & Cognition | Crowley et al 2021
A Reduction in Behavioural Pattern Separation Is Attenuated by Dietary Supplementation with a Magnesium-Rich Marine Mineral Blend in Middle-Aged Rats
MAGNESIUM RESEARCH | Felice et al., 2018
Bioaccessibility and Bioavailability of a Marine-Derived Multimineral, Aquamin-Magnesium